8 Types of Ecommerce Warehouses and How to Set Up Your Own

موعد التسليم is one of the biggest factors in ecommerce success. Shoppers today expect speed, and the bar keeps getting higher. In a 2024 survey, most respondents said they wanted their packages delivered within two days. To meet that demand and keep customers satisfied, the ecommerce warehouse plays a central role. It is the place that determines how fast, accurate, and reliable your fulfillment can be.
Of course, not every seller starts with a full warehouse. Many new online businesses begin with products stacked in a spare room or garage. But as sales increase, that setup quickly shows its limits. That is when sellers need a proper ecommerce warehouse and a clear grasp of ecommerce warehouse management to keep operations running smoothly.
In this blog, we will explore what ecommerce warehousing means, the different types of ecommerce warehouses, and how to set up and manage an ecommerce warehouse effectively.
What is ecommerce warehousing?

Ecommerce warehousing is the process of storing and managing products before they are sold and shipped to customers. It is more than just stacking boxes on shelves. A good ecommerce warehouse manages every step your inventory goes through before it reaches the customer. That includes keeping products safe, tracking what you have in stock, and preparing orders for fast delivery.
8 Types of Ecommerce Warehouses
Choosing the right type of ecommerce warehouse depends on the size of your عمل and your specific needs. Some businesses want full control over their storage space, while others prefer flexibility or a more cost-effective option. Understanding the differences helps you avoid paying for space you do not need or struggling with limited capacity.
Here are eight common types of ecommerce warehouses:
Public warehouses
A public warehouse is a large facility usually managed by a third-party company. Businesses can rent space in these warehouses, paying based on the amount of area or volume they use. Space can be rented for short-term or long-term needs, making it a flexible option.
For instance, a business may need extra storage during the holiday season but not for the rest of the year. In this case, a public warehouse provides an affordable solution without requiring a permanent commitment.
Public warehouses work well for small sellers or seasonal businesses. They are cost-effective and flexible, although they provide less control over daily operations.
Private warehouses

A private warehouse is a storage facility owned by an individual company rather than a third-party provider. These warehouses allow businesses to design the layout to fit their exact needs, making sure products are handled, stored, and protected properly.
For example, Walmart operates its own large warehouse network. This setup helps the company manage inventory more effectively while also keeping transportation costs lower.
Private warehouses are best suited for large retailers or established brands with steady demand. They offer maximum control and long-term stability, but they also come with high upfront costs and ongoing operating expenses.
Fulfillment centers
A fulfillment center is a third-party service provider that stores products for a short time, processes orders, and ships them directly to customers. By outsourcing order fulfillment, sellers avoid the high costs of building and managing their own warehouses.
Here is how it usually works: when a customer places an online order, the fulfillment center receives the request, picks the product from storage, packs it, and ships it to the buyer.
تحقيق، إنجاز centers are a great choice for ecommerce sellers who want faster delivery and access to professional systems without having to manage everything themselves.
Cooperative warehouses
A cooperative warehouse is a shared facility owned and operated by a group of businesses, often from the same industry or local area. These businesses usually have similar needs and goals, so they join forces to manage storage together.
This model creates a sense of community and shared responsibility. At the same time, decision-making can be slower or more complicated because all members need to agree on how the warehouse is run.
Consolidation warehouses
A consolidation warehouse is a third-party logistics facility that combines smaller shipments from different suppliers into one larger, cost-efficient load. The products are grouped by destination or type before being shipped out together.
For example, if three separate shipments are headed to the same city, they do not need to be sent individually. Instead, they are first delivered to the consolidation warehouse, where they are combined and shipped as one. This method helps lower transportation costs for businesses.
Smart warehouses
A smart warehouse uses advanced technology and modern management systems to digitize and automate storage and order processing. Tools such as artificial intelligence, automation, Internet of Things applications, and data analytics are often part of the system. These features make operations faster and more accurate.
However, smart warehouses require high setup and maintenance costs, which may be a barrier for small businesses. They are best suited for companies with large-scale operations that can benefit from advanced efficiency.
Government warehouses
A government warehouse is owned and operated by public authorities and is available for both individuals and businesses. These facilities are usually large, well-regulated, and highly secure. They may also include special areas such as temperature-controlled storage, security monitoring, or hazardous material sections.
The main advantages are security and reliability, but government warehouses often come with strict rules and less flexibility compared to private options.
Reverse logistics warehouses
A reverse logistics warehouse is designed to handle returned products. Instead of moving goods out to customers, it focuses on items that come back into the supply chain. Products may be inspected, repaired, repackaged, recycled, or disposed of, depending on their condition.
For example, if customers return clothing that does not fit, the warehouse processes the يعود, checks the quality, and either restocks the item or prepares it for resale at a discount. This type of facility is especially important for ecommerce sellers, since returns are a normal part of online shopping.
How to set up an ecommerce warehouse?
Building an efficient ecommerce warehouse is not as simple as stacking products on shelves. It takes careful planning to make sure everything runs smoothly. Here are four key steps to help you set up your warehouse.
1. Plan your warehouse space
Before setting up or renting a warehouse, you need to think about how much space your business really needs. A well-organized warehouse is usually divided into different zones, such as receiving, storage, picking, packing, and shipping. Each area should have enough room to handle its specific task without getting in the way of other operations. Good layout planning not only keeps the warehouse safe but also makes the workflow much faster.
2. Get the right equipment
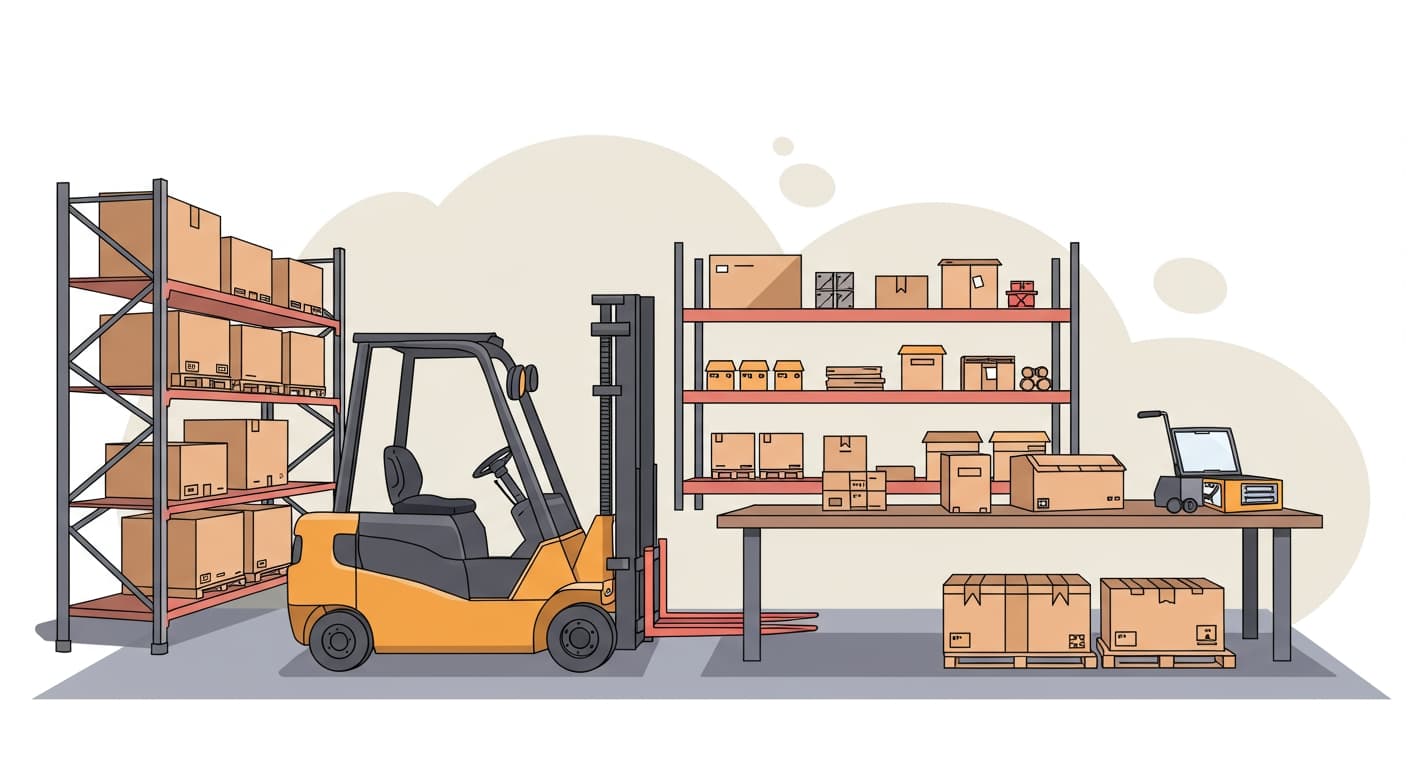

Having the right equipment is essential for an efficient ecommerce warehouse. The tools you need depend on your business size, your sales volume, and the types of products you store. Different categories of products may require different equipment.
Basic warehouse equipment usually falls into four groups:
- Storage equipment: shelves, lockers, small storage bins
- Handling equipment: forklifts, pallet jacks, carts
- Packing and shipping materials: bubble wrap, cardboard boxes, tape
- Inventory management tools: software to track stock and orders
Some products, like perishable food, may also need specialized equipment, such as refrigeration or freezers. You can also choose to rent a warehouse that already comes equipped with the necessary tools, which can save a lot of time and hassle.
3. Set clear warehouse guidelines

If you hire staff to work in your warehouse, it’s important to set clear guidelines from the start. This includes creating policies for safety, workflow, and quality control. Employees should know how to handle products properly, follow order picking and packing procedures, and maintain accuracy in inventory management. Clear guidelines not only keep the warehouse organized and safe but also help prevent mistakes that can affect your customers.
4. Optimize workflow and inventory management

Once your warehouse layout is set and staff are trained, the next step is to make sure operations run smoothly and جرد is managed effectively. Every product in the warehouse should be organized, and the quantity of each SKU should be accurately tracked at all times.
Balancing the flow of products from manufacturers to customers can be one of the trickiest parts of managing an ecommerce business. The key is inventory management: keeping just the right amount of stock in the warehouse so orders can be fulfilled quickly without creating excess storage. This requires accurate forecasting of order volumes, clear communication with suppliers and shipping partners, and reliable tools to track inventory in real time.
For businesses storing inventory in multiple warehouses, it’s important to have a strong distributed inventory strategy. This means planning, resources, and tools to make sure every warehouse has the right products in the right amounts.
Even though some warehouses still count items manually, modern technology allows faster scanning and tracking of products. A good warehouse should have systems in place to see stock levels at any moment, helping to avoid overselling or delays caused by out-of-stock items.
Optimizing workflow and inventory management improves speed, reduces errors, and ensures your warehouse can keep up with customer demand.
Start Dropshipping without Holding Stock
Managing an ecommerce warehouse can be complex and requires time, resources, and careful planning. Tracking every SKU, forecasting demand, and fulfilling orders on time can be challenging, especially for small or growing businesses. But with إسقاط الشحن, you can run an online store without holding your own stock.
مع Sup Dropshipping, products are stored and shipped directly by trusted suppliers. This means you don’t need to rent a warehouse or invest in inventory upfront. When a customer places an order, the product is picked, packed, and shipped by the supplier, letting you focus on marketing, customer service, and growing your business.
Beyond fulfillment, Sup Dropshipping gives you access to a wide range of high-quality products and reliable suppliers. You can test different products without financial risk, scale up as sales grow, and offer fast, dependable shipping that keeps customers satisfied and loyal.
In short, dropshipping through Sup Dropshipping lets you start selling online with lower upfront costs, fewer operational headaches, and more flexibility, all while avoiding the challenges of traditional warehouse management. To learn more or get started, اتصل بنا اليوم.
Ecommerce warehouse FAQs
1. What are the types of ecommerce?
There are eight common types of ecommerce warehouses:
- Private warehouses
- Public warehouses
- Fulfillment centers
- Cooperative warehouses
- Consolidation warehouses
- Smart warehouses
- Government warehouses
- Reverse logistics warehouses
2. Should I invest in my own warehouse?
It depends on the size and stage of your business. Small or growing ecommerce sellers might find renting space or using a fulfillment service more cost-effective, while larger businesses with steady demand may benefit from owning a warehouse.
3. Is a warehouse the same as a fulfillment center?
A fulfillment center is actually a type of ecommerce warehouse, but it does more than just store products. While a typical warehouse mainly focuses on storage, sometimes for months or even years, a fulfillment center also provides services like receiving and processing goods, picking and packing orders, assembly, labeling, and shipping. In short, all fulfillment centers are warehouses, but not all warehouses function as fulfillment centers.
عن المؤلف

يمكن
ماي هي مدوّنة في Sup Dropshipping وتتمتع بخبرة تزيد عن 5 سنوات في مجال التجارة الإلكترونية. إن شغف ماي بالتجارة الإلكترونية يدفعها إلى البقاء على اطلاع بأحدث الاتجاهات ومشاركة خبراتها معك من خلال مدونتها. تحب في أوقات فراغها قراءة رواية أو الدردشة مع الأصدقاء.




اترك تعليقاً